Categories
Scope of application
From the analysis of product characteristics, semiconductor refrigeration fins are commonly used in refrigeration and heating fields:
Military and aerospace: infrared detection, navigation, and thermoelectric power generation systems for radars, submarines, rockets, satellites, etc.
Medical treatment: cold force, cold fusion, cataract extraction instrument, blood analyzer, etc.
Laboratory equipment: cold traps, cold boxes, cold baths, electronic low-temperature test devices, various constant temperature, high and low temperature experimental instruments
Special equipment: low temperature tester for petroleum products, low temperature tester for biochemical products, bacterial incubator, constant temperature developing tank, computer, etc.
Daily life: air conditioners, hot and cold boxes, water dispensers, electronic communications, thermoelectric power generation, semiconductor hot and cold fans, cold and hot compress eye protectors, laser freezing point hair removal devices, etc.
Product Overview
Semiconductor Refrigerator, also called thermoelectric coolers, are a kind of heat pump. Its advantage is that there are no sliding parts, and it is used in some occasions where space is limited, reliability is high, and there is no refrigerant pollution.
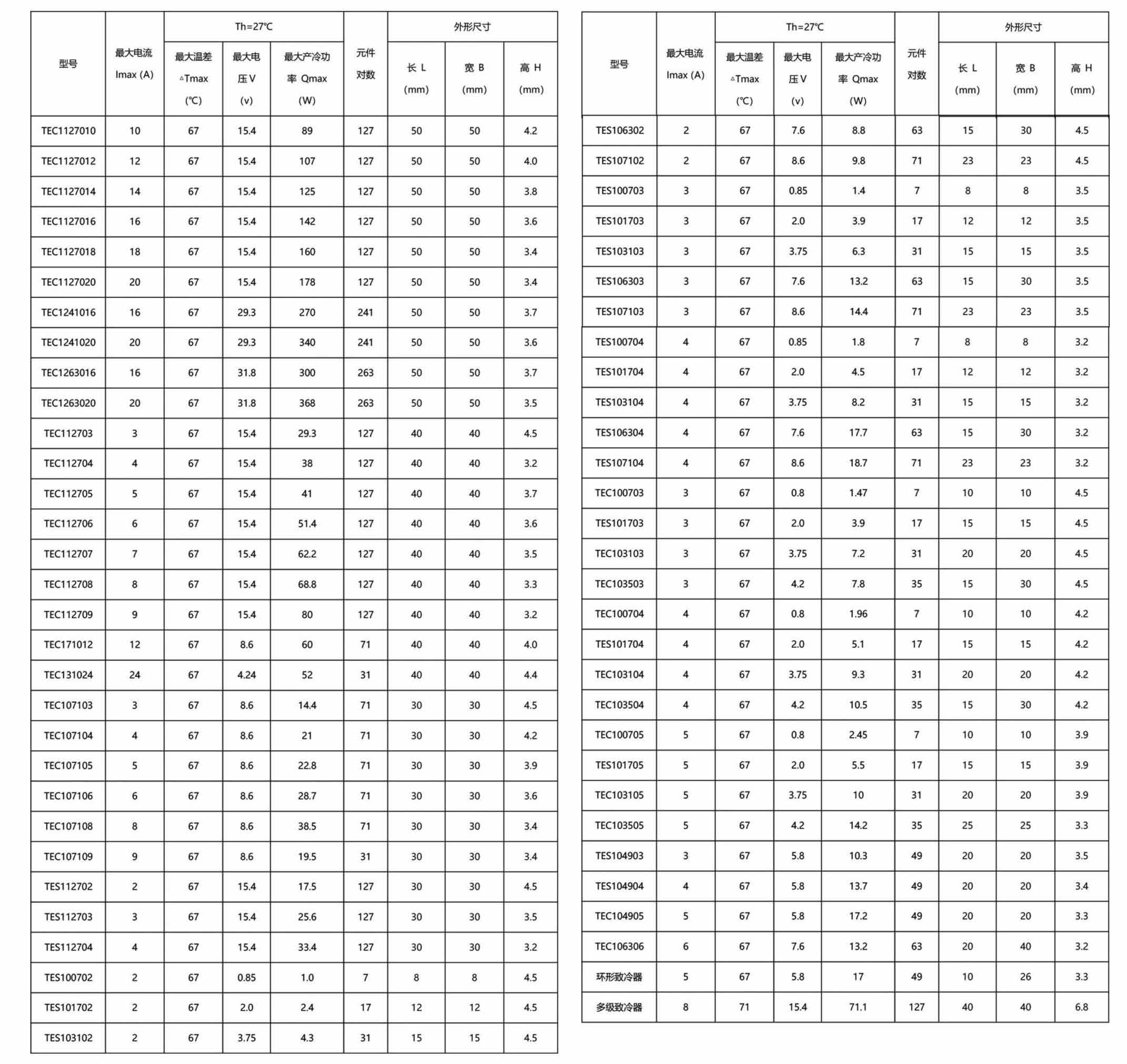
The working operation of the semiconductor refrigeration chip uses direct current, which can be used for both cooling and heating. By changing the polarity of the direct current, it is determined to realize cooling or heating on the same refrigerator. This effect is produced by the principle of thermoelectricity. , The following picture is a monolithic refrigerator, which is composed of two ceramic plates, between which there are N-type and P-type semiconductor materials (bismuth telluride). This semiconductor element is connected in series in the circuit.
Principle Of Operation
When a piece of N-type semiconductor material and a piece of P-type semiconductor material are connected to form a galvanic pair, when a DC current is connected in this circuit, energy transfer can occur. The current flows from the N-type element to the P-type element to absorb heat. As the cold end, the joint that flows from the P-type element to the N-type element releases heat and becomes the hot end. The magnitude of heat absorption and heat release is determined by the magnitude of the current and the number of pairs of semiconductor materials N and P. The following three points are the thermoelectric effect of thermoelectric cooling.
1. Seebeck effect (SEEBECK EFFECT)
In 1822, the German Seebeck discovered that when two different conductors are connected, if the two connection points maintain different temperature differences, a thermoelectric force will be generated in the conductor:ES=S.△T; where: ES Is the thermoelectromotive force S is the thermoelectromotive force rate (Seebeck coefficient) △T is the temperature difference between the contacts
2. Peltier effect (PELTIER EFFECT)
In 1834, the French Peltier discovered the effect of the Seebeck effect, that is, when the current flows through the junction formed by two different conductors, the junction will produce heat release and heat absorption, and the magnitude of the heat release or absorption. Determined by the size of the current.
Qл=л.I л=aTc
In the formula: Qπ is the heat release or heat absorption power I is the working current a is the thermoelectromotive force Tc is the cold junction temperature
3. Thomson effect (THOMSON EFFECT)
When current flows through a conductor with a temperature gradient, in addition to the Joule heat generated by the resistance of the conductor, the conductor also releases or absorbs heat. Between the two points of the conductor with a temperature difference of △T, the heat release or absorption is :
Qτ=τ.I.△T
Qτ is the heat release or heat absorption power τ is the Thomson coefficient I is the working current △T is the temperature gradient
1. There are no sliding parts, it is a solid piece, there is no vibration, noise, long life, and easy installation;
2. It does not need any refrigerant, it can work continuously, there is no pollution source, no rotating parts, and no rotation is easy;
3. The semiconductor refrigeration film has two functions, which can be used for cooling and heating. The cooling efficiency is generally not high, but the heating efficiency is very high. Therefore, a single piece can replace the separate heating system and the cooling system;
4. The semiconductor refrigeration chip is a current-transducer type chip. Through the control of the input current, high-precision temperature control can be realized. Coupled with temperature detection and control methods, it is easy to realize remote control, program control, and computer control, which is convenient to form automatic control system;
5. The thermal inertia of the semiconductor cooling fin is very small, and the cooling and heating time is very fast. When the hot end has good heat dissipation and the cold end is empty, the cooling fin can reach the rated temperature difference in less than one minute;
6. The reverse use of semiconductor refrigeration fins is thermoelectric power generation. Semiconductor refrigeration fins are generally suitable for power generation in the middle and low temperature areas;
7. The power of a single refrigeration element of the semiconductor refrigeration film is very small, but it is combined into a stack, and the same type of stack is used in a series or parallel method to form a refrigeration system, the power can be made very large, so the cooling power can be made In the range of a few milliwatts to tens of thousands of watts;
8. The temperature difference range of the semiconductor refrigeration sheet can be realized from a positive temperature of 90°C to a negative temperature of 130°C.
Number Naming Reference

Instructions For Use
1. The heat dissipation of semiconductor refrigeration fins is a professional technology, and it is also the basis for the long-term operation of semiconductor refrigeration fins. Good heat dissipation is the prerequisite for obtaining the lowest cold junction temperature. Heat dissipation methods include: natural heat dissipation, liquid-filled heat dissipation, forced air cooling heat dissipation, and vacuum latent heat dissipation;
2. The semiconductor refrigeration sheet works by inputting a DC power supply and must be equipped with a dedicated power supply: DC power supply, AC current, the working voltage and current of the semiconductor refrigerator must meet the needs of the working device, and the refrigerator must be energized during the cold and heat exchange When both ends return to room temperature (usually it takes more than 5 minutes to proceed);
3. The cooling fins should be placed flat and in full contact with the surface of the cold storage plate and aluminum radiator when using, otherwise the cooling effect will be affected.
4. Avoid working outside the range of over-temperature zone, and avoid frequent rapid heating (≥70℃) and rapid cooling (≤10℃), so as not to cause internal cracking of the crystal, failure, or shorten the service life.
5. The refrigeration sheet has a tight sealant and good waterproof performance. The sealant must not be damaged until water invades during use, otherwise it will cause an internal short circuit and fail.
6. The refrigeration sheet is a fragile product. Strong impact and falling from a high place may damage the refrigeration sheet. Please install it carefully.
7. The refrigeration sheet should usually be stored in a dry, ventilated, and non-corrosive environment with a relative humidity of less than 80% and a relative humidity of -10 to +40°C.
Dimensions
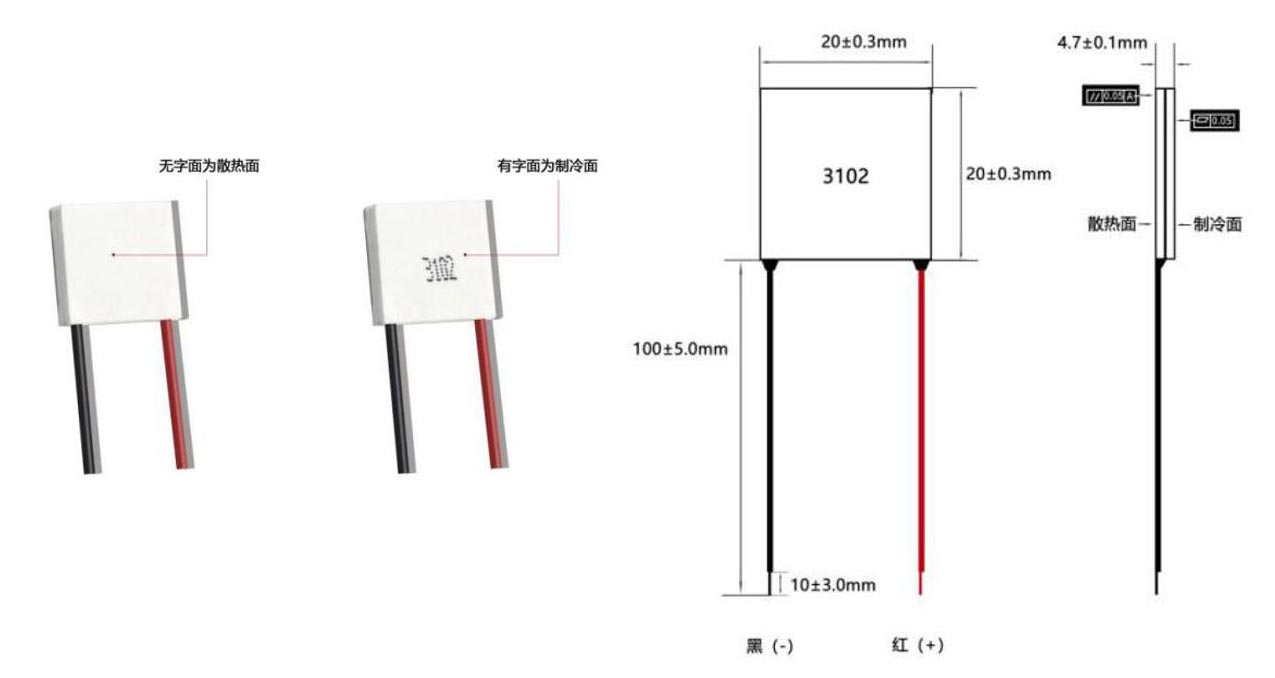
The size can be customized according to customer requirements
Approximate value is only used to select samples for certification test
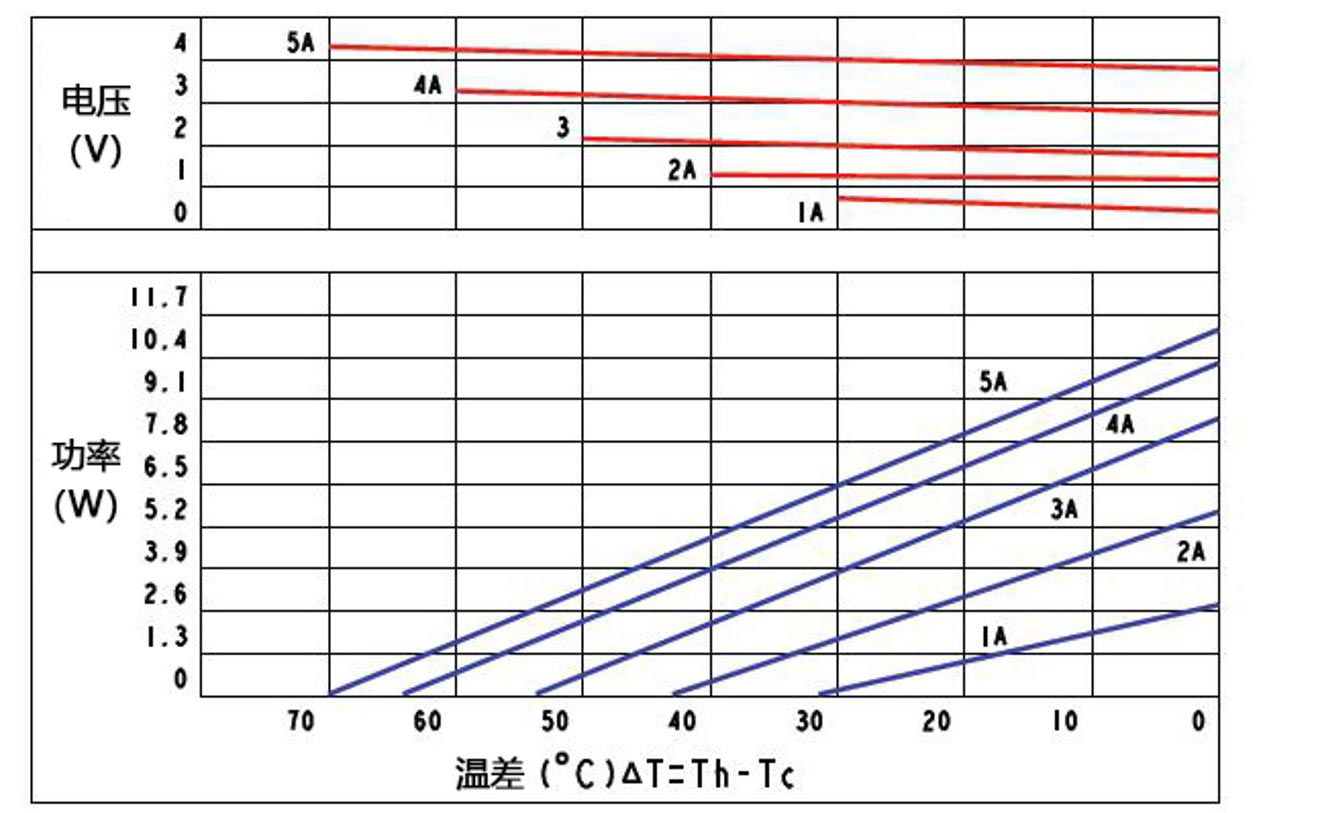
Technical Parameters